Automated volumetric MR imaging provides an opportunity to implement brain structure volume measurements to assess symptoms of potential Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in patients by analyzing the volumes of behavioral control regions, which can then be evaluated over time.
In ADHD patients, reduction in the whole brain volume, as well as reduction in regional structure volumes, such as those in the basal ganglia, and frontal and temporal lobes, have been correlated with attention control or hyperactivity-impulsivity. According to several studies, whole brain and subcortical volume measurements provide valuable biomarkers for clinicians when evaluating possible ADHD patients as young as 4 years old.
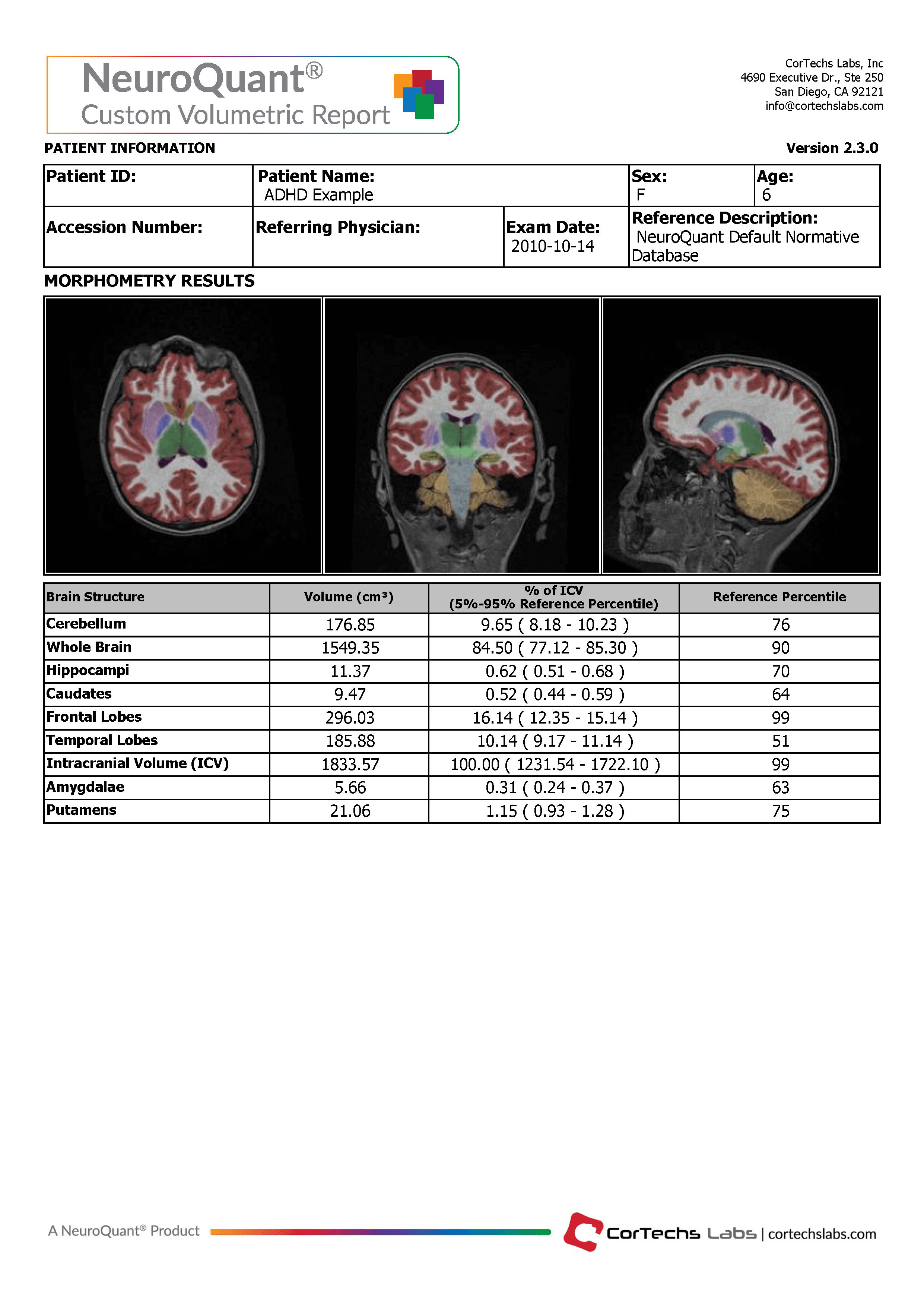
The NeuroQuant Custom Volumetric report is applicable for patients 3 to 100 years old and provides volume measurements for up to nine clinician-selected brain structures. Additionally, the clinician is able to review axial, coronal, and sagittal DICOM images in which the segmented brain structures are given a color overlay.
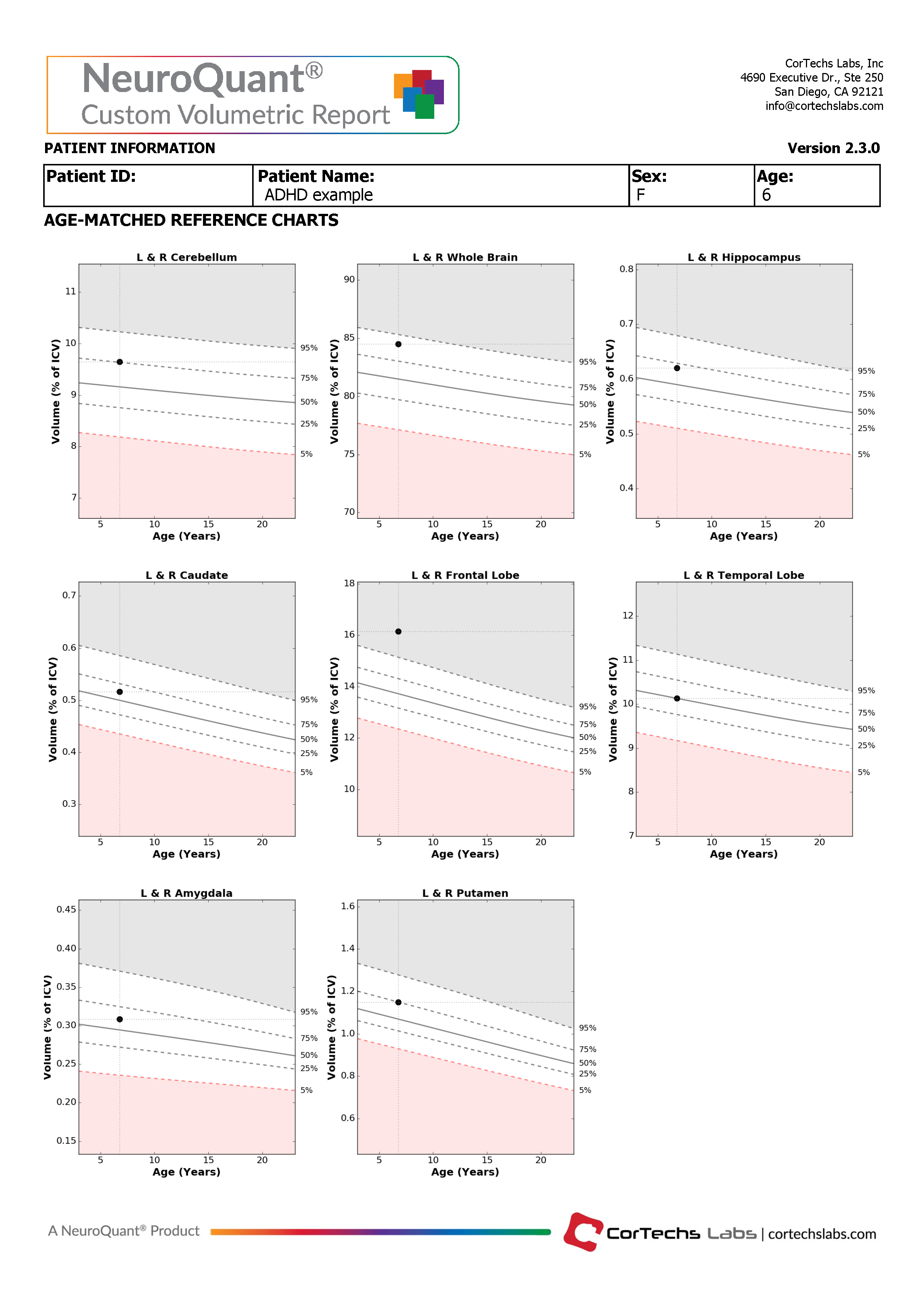
The Custom Volumetric report indicates the patient’s brain structure volume measurements compared to a healthy population via Cortechs.ai’ normative reference data . This allows NeuroQuant to deliver a precise indication of where that individual’s brain structure volumes lie relative to an age- and gender-based reference chart.
The NeuroQuant Custom Volumetric report provides a multi time point feature used to assess volume change over time in these brain regions by displaying the results of the current measurement together with all previous measurements on the normative reference charts. Physicians can use this information to quickly and easily evaluate longitudinal change in several brain structures.
Jacobson, L., Crocetti, D., Dirlikov, B., Slifer, K., Denckla, M., Mostofsky, S., & Mahone, E. (2018). Anomalous Brain Development Is Evident in Preschoolers With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 1-9. doi:10.1017/S1355617718000103
Hoogman, Martine et al. (2017) Subcortical brain volume differences in participants with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adults: a cross-sectional mega-analysis. The Lancet Psychiatry. 4(4) :310 – 319
Curatolo et al. (2010) The neurobiological basis of ADHD. Italian Journal of Pediatrics 36:79