How NeuroAlign CT Subtraction Maps Enhance Detection and Confidence in Neuroradiology
“I can’t remember life without NeuroAlign CT, and frankly, I don’t want to! The perfectly aligned and reformatted images that I get with NeuroAlign CT make my interpretation of head CTs more efficient and more accurate. The subtraction images that NeuroAlign CT provides help me to quickly and accurately assess changes.”
— Dr. Nikdokht Farid, MD, Neuroradiologist, UC San Diego Health
In the realm of neurological imaging, CT has taken a seat at the head of the table in the detection and ongoing assessment of life-threatening pathologies. But what if head CT assessment could be even faster and more accurate?
NeuroAlign CT is a powerful head CT tool with multiple features, including automatic image alignment and reformating, volumetric reports, and subtraction maps. One of its most valuable features is the generation of subtraction images—a capability highly regarded by neuroradiologists. These subtraction maps, automatically generated by NeuroAlign CT software, allow for improved detection and visualization of subtle interval changes. By improving conspicuity and standardizing image alignment, NeuroAlign CT strengthens diagnostic confidence,efficiency, and accuracy.
What are subtraction maps?
NeuroAlign CT subtraction maps provide a clear visualization of longitudinal changes. While the concept is simple, its beauty lies in the ability to easily highlight areas of change between two timepoints. NeuroAlign CT subtraction maps show subtle density changes by calculating change in HU (Hounsfield Units) at the voxel level. Current exams are automatically aligned and reformatted with prior exams in standardized space to enable this analysis. An additional removal of skull and non-brain tissue from the subtraction image provides an easily interpretable series that allows for visualizing evolving pathology.
How Does It Work?
CT imaging is based on Hounsfield Units (HU), a standardized measure of tissue density. Each voxel in a CT scan represents a small volume of tissue with a specific HU value.
NeuroAlign CT’s subtraction maps are generated through a structured, multi-step process:
- Alignment and Reformatting of Serial CT Exams – The algorithm precisely aligns prior and current scans in a standardized AC-PC plane to ensure accurate spatial correspondence.
- Voxel-by-Voxel Subtraction – The HU values of corresponding voxels from the prior scan are subtracted from the current scan, highlighting density differences.
- Enhanced Visualization of Subtle Changes – The resulting subtraction images are further filtered to remove the skull to improve visualization and the detection of interval changes that might otherwise go unnoticed in standard side-by-side comparisons.
Clinical Applications: Case Studies
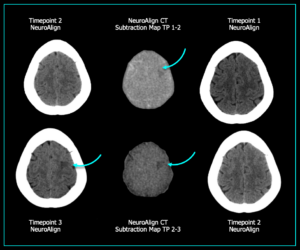
Case Study 1: Identifying an Acute Ischemic Stroke Earlier
The images below represent three sequential head CT scans of a patient evaluated over time. At timepoint 3, a well-defined stroke is clearly visible, making the diagnosis straightforward. However, at timepoint 2, an ischemic stroke was present but not conspicuous on conventional imaging. This finding could easily be overlooked, particularly when manually comparing non-co-registered scans.
In NeuroAlign CT’s subtraction map between timepoints 1 and 2, a subtle hypodensity is detected in the left frontal region—an early change that is not easily visualized on the standard images from timepoint 2. By enabling early detection before the stroke was severe enough to be seen in a standard side-by-side comparison, NeuroAlign CT provides a crucial advantage — helping clinicians intervene sooner and reducing the risk of a missed diagnosis.
Case Study 2: Utilizing NeuroAlign CT for Precise Ventricular Volume Assessment
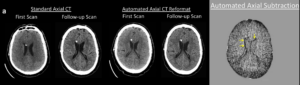
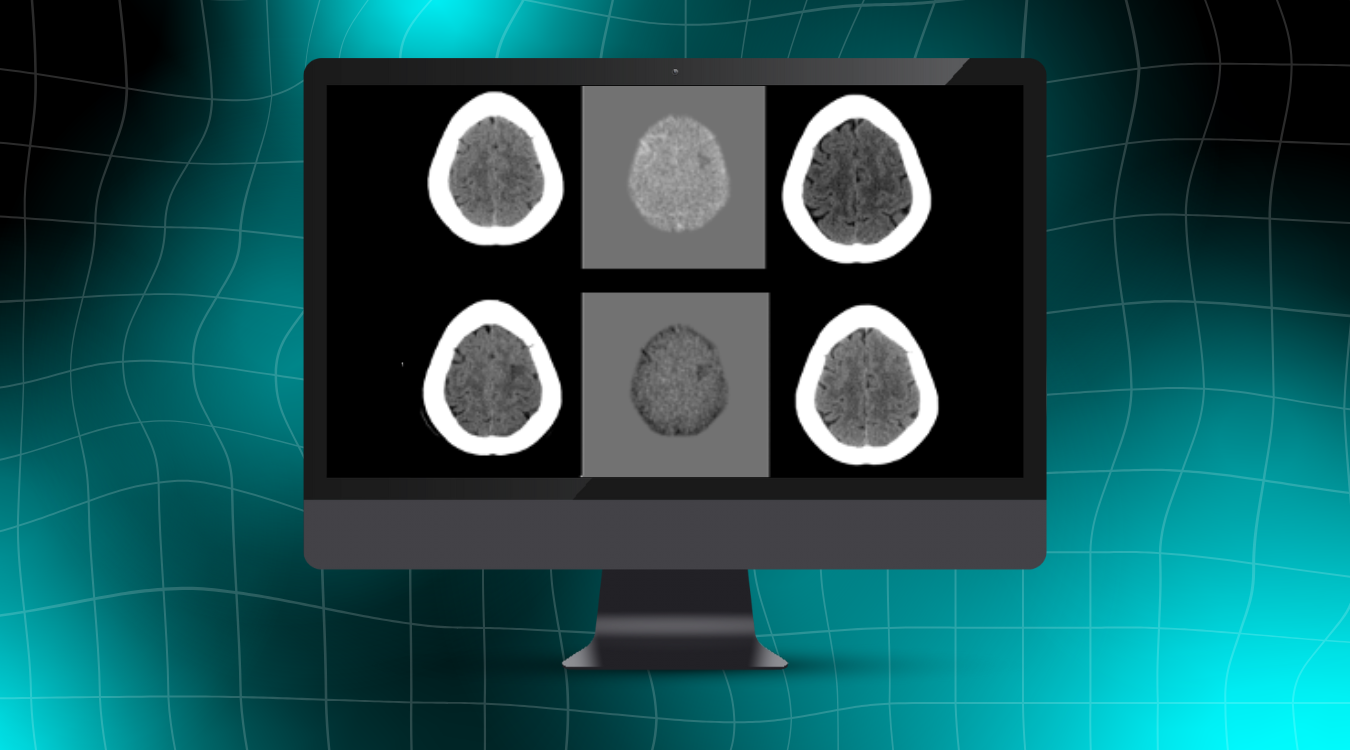
Figure 1: Non-contrast head CT demonstrating automatic subtraction.[1]
NeuroAlign CT is also a valuable tool for assessing ventricular changes over time. In the example above, the subtraction map highlights ventricular enlargement by outlining the expansion with a distinct hypodense signal, making these changes easy to visualize.
Conversely, in the example below, longitudinal evaluation reveals a reduction in ventricular size, indicated by the hyperdense border surrounding the ventricles in the subtraction series. This precise visualization aids in tracking ventricular dynamics, providing critical insights for clinical assessment and decision-making.
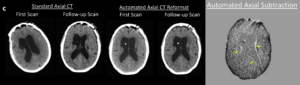
Figure 2: Non-contrast head CT demonstrating automatic subtraction.[2]
Case Study 3: Evaluating Hemorrhagic Changes
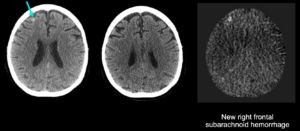
Figure 3: New right frontal subarachnoid hemorrhage
NeuroAlign CT subtraction maps can aid in the identification and evaluation of hemorrhagic changes. In the case study above, subtraction maps showed a right frontal hyperdensity consistent with hemorrhage.
In addition to increased visibility of hemorrhages, NeuroAlignCT subtraction maps provide greater speed, confidence, and accuracy among radiologists. In a study performed by Hseih, et al., researchers found that radiologists were able to interpret ICH changes 34% faster with NeuroAlign CT (71 vs 98 seconds). This study also demonstrated increased confidence in determining changes in ICH, as well as a 13% improvement in accuracy for detecting cases with increased ICH.[3]
Case Study 4: Identifying Parenchymal Changes in Brain Trauma
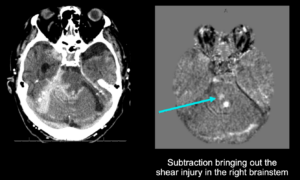
Figure 4: Right brainstem shear injury
In the example above, subtraction maps enhanced the conspicuity of a right brainstem shear injury.
Conclusion
NeuroAlign CT provides neuroradiologists with an advanced solution for detecting subtle changes that might otherwise go unnoticed. By offering precise standardized formatting and alignment, subtraction imaging, and enhanced visualization of interval findings, it improves diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and clinical confidence. With NeuroAlign CT, subtraction maps do the hard work so that radiologists can deliver more definitive assessments, ensuring that no critical finding is overlooked.
References:
- Figure 1: Yamin, et all, Automated CT registration tool improves sensitivity to change in ventricular volume in patients with shunts and drains. BJR, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20190398
- Figure 2: Yamin, et all, Automated CT registration tool improves sensitivity to change in ventricular volume in patients with shunts and drains. BJR, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20190398
- Hseih, et al., Assessment of an Automated CT Registration and Subtraction Tool to Improve Radiologic Evaluation of Patients with Intracranial Hemorrhage [abstract]. Presented at: Western Neuroradiological Society; October 17-20, 2024; Kona, Hawaii.