By
Cortechs.ai
2 mins
 On Saturday, October 17, in San Diego, the Cortechs.ai team joins over 2,300 walkers and 350 teams for the Alzheimer’s Association’s Walk to End Alzheimer’s®, the nation’s largest event to raise awareness andfunds to fight Alzheimer’s disease.
On Saturday, October 17, in San Diego, the Cortechs.ai team joins over 2,300 walkers and 350 teams for the Alzheimer’s Association’s Walk to End Alzheimer’s®, the nation’s largest event to raise awareness andfunds to fight Alzheimer’s disease.
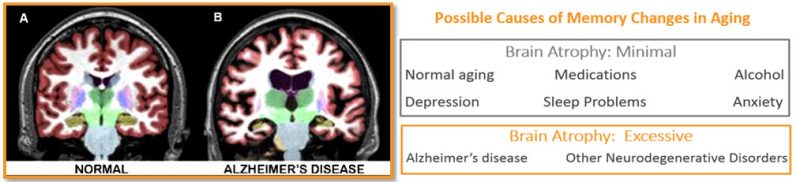
Dementia is a general term for brain conditions and diseases that can cause a slow, progressive, decline of cognitive ability. The loss of brain volume due to atrophy of brain cells (neurodegeneration) is the most common cause of dementia conditions. Brain volume loss is seen in Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia (Pick’s disease), Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and dementia with Lewy bodies.
Other conditions and diseases can imitate the signs and symptoms of dementia, as well as co-exist with neurodegenerative dementia making diagnosis more difficult. Some examples of these, more treatable, causes include:
- Vascular dementia (from blocked or reduced blood flow to the brain)
- Metabolic conditions (such as hypothyroidism, vitamin B12 deficiency, and Addison’s disease)
- Toxicity due to drugs or alcohol
- Infections of the brain (such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, HIV, and neurosyphilis)
- Hydrocephalus (a buildup of cerebral spinal fluid in the brain)
- Brain tumors and cancers of the central nervous system
- Traumatic brain injury
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is by far the most common form of dementia at roughly 70% of all dementia cases. While the majority of patients with AD are older than 65 years, up to 5% of people diagnosed are in their 40s to 50s.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can be used to confirm suspected neurodegeneration, such as AD, and can help to rule out other conditions. A MRI provides visualization of the brain structures to help in the evaluation of neurodegeneration, specifically the hippocampus. Patients with mild cognitive impairment who have an unusually small hippocampal volume, are 2-4 times more likely to progress to AD in 2 to 3 years, as compared to patients with larger hippocampal volume.
NeuroQuant® is a leading medical device software for volumetric MRI processing, providing automatic image segmentation of brain structures. NeuroQuant uses the images from the MRI scan to measure the volume of certain brain structures. For patients with cognitive impairment and memory loss, volume measurements of the hippocampus, inferior lateral ventricles and the hippocampal occupancy score (HOC) are reported, providing important information in the assessment of neurodegenerative dementia.
Please consider donating to help the Alzheimer’s Association’s goal to advance research to treat and prevent Alzheimer’s, and provide programs and support to improve the lives of millions of affected Americans. Click here to learn more about the Alzheimer’s Association.
- American Academy of Neurology. “Shrinking In Hippocampus Area Of Brain Precedes Alzheimer’s Disease.” ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 17 March 2009.
- McEvoy, L. K. & Brewer, J. B. (2012). Biomarkers for the clinical evaluation of the cognitively impaired elderly: amyloid is not enough. Imag. Med, 4(3), 14.
- Alzheimer’s Association. www.alz.org
Share