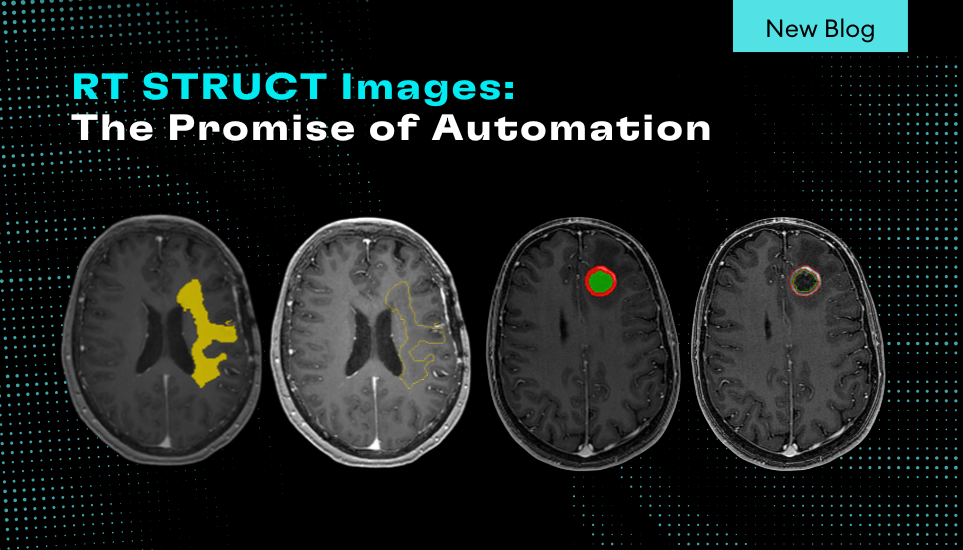
In this post, I review additional causes affecting goodness of fit which can result in NeuroQuant being unable to segment specific brain structures and issuing a processing error message. Previous posts discussed why contrast agents are not used to achieve quality segmentation with NeuroQuant, and examined why good alignment to atlas is necessary for accurate NeuroQuant output.
Ensuring proper processing is an important factor in NeuroQuant’s analysis process. To achieve its high quality segmentation results, NeuroQuant verifies each patient’s brain image can be processed correctly. This safeguards the accuracy of the segmentation results and therefore, the accuracy of the calculated volumes.
Patients who have shunts, implants or other artifacts or inherent abnormalities, can potentially generate segmentation misregistration. To prevent such errors and protect the accuracy of the results, NeuroQuant prevents analysis when such artifacts or anatomical anomalies are present.
In some cases, such as the first example below, a shunt in the patient’s brain made good alignment to atlas impossible, resulting in a processing failure.
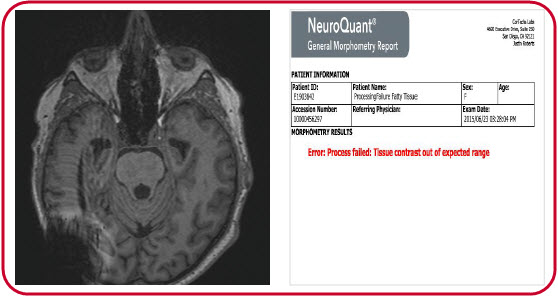 In the second example, a patient’s excess cranial tissue prevented proper processing and resulted in an error message.
In the second example, a patient’s excess cranial tissue prevented proper processing and resulted in an error message.
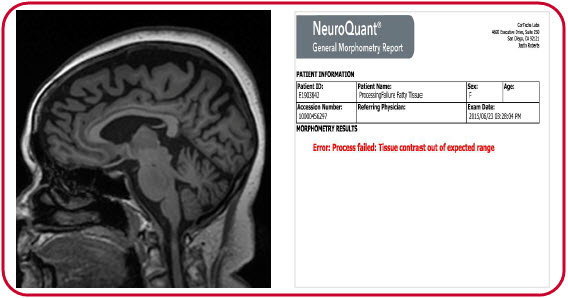 More information about using and processing NeuroQuant can be found here.
More information about using and processing NeuroQuant can be found here.