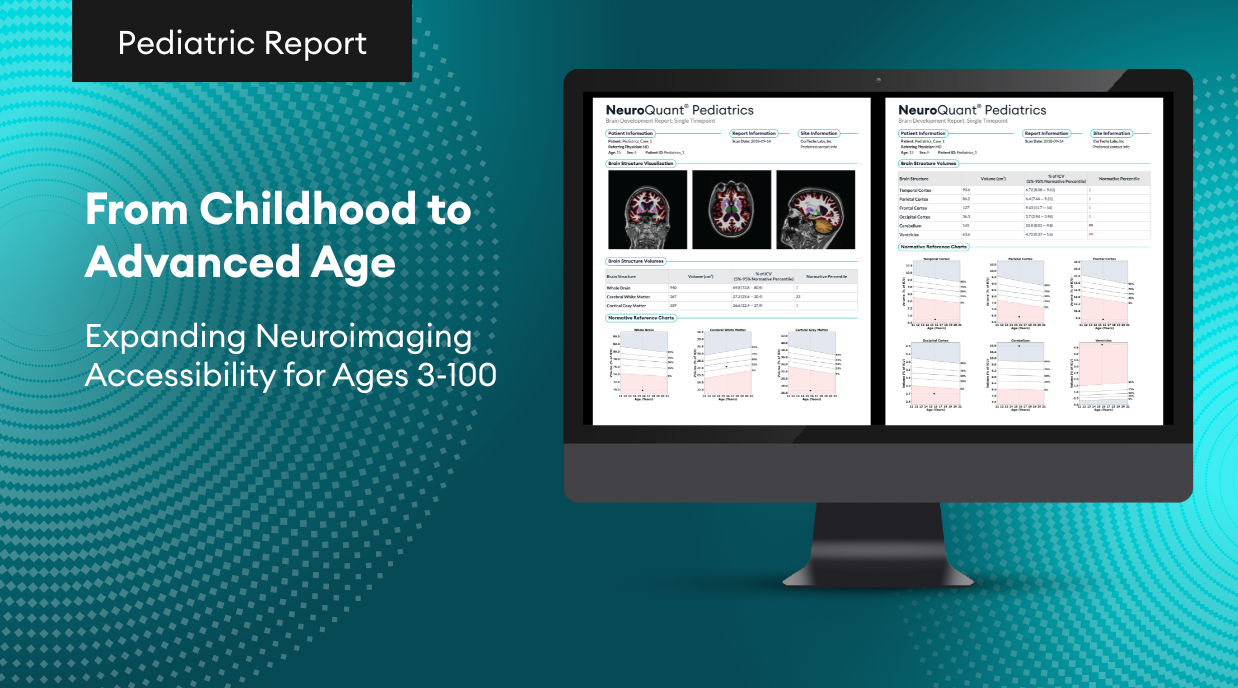
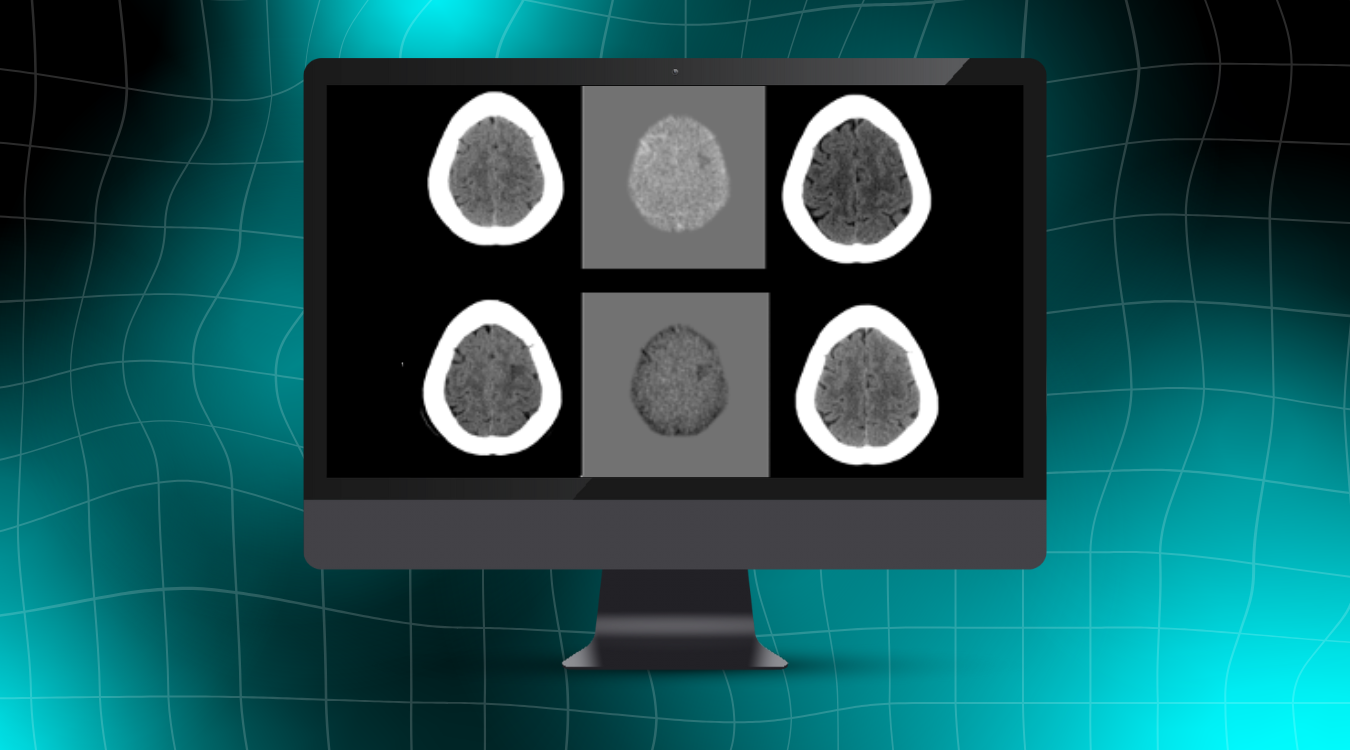
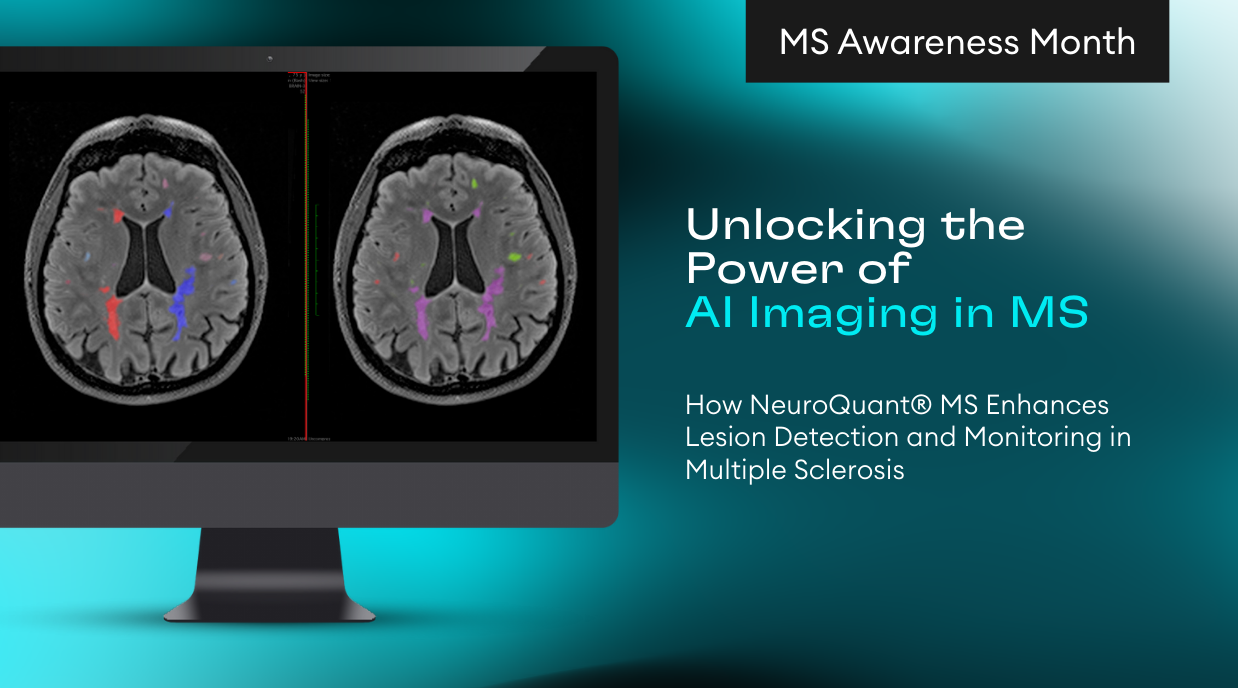
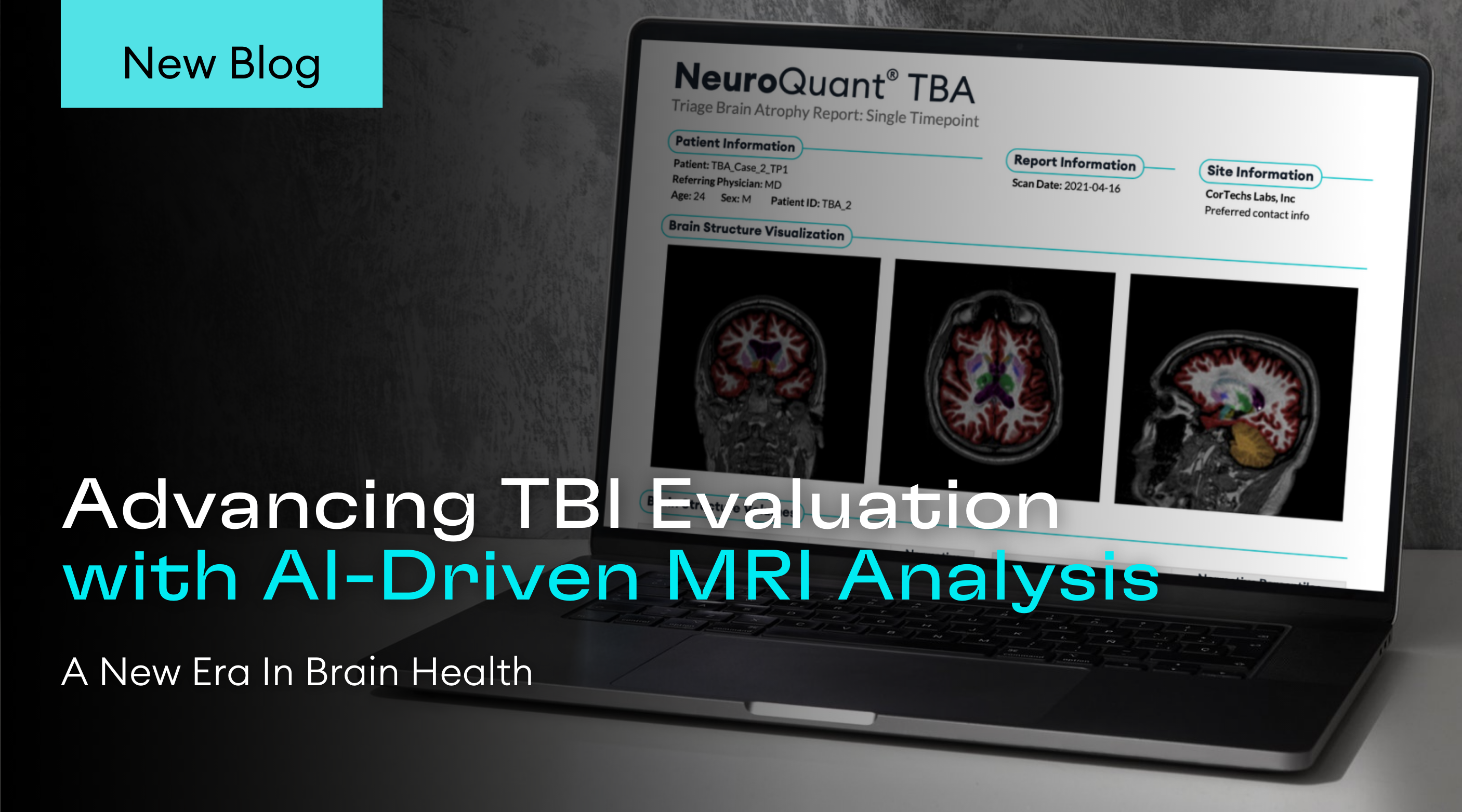
Quantitative measurements of lesion volume and lesion distribution have significant value for clinicians evaluating disease progression. Subjective measurements based on a clinician’s visual inspection and manual lesion segmentation are often vulnerable to inter-and intra-rater variability, resulting in low reproducibility. Thus, objective, automated lesion segmentation tools have been developed [1-3] to overcome these problems. Since the appearance of lesions may vary across different MRI protocols, incorporating multiple MRI studies provides more information to accurately delineate lesions.